Polyrhythmia
What is polyrhythmia?
 |
polirritmia   |
Polyrhythm is the superposition of two or more rhythmic voices, each with their respective temporal successions. The interrelation between the different voices generates a new succession resulting from the integration of all the voices.
This new fusionated succesion (obtained through the fusion operation) allows us to see more clearly how the iTs of the different voices interact:
 |
sucesión fusionada   |
Cases of polyrhythmias
There are different cases of polyrhythms according to the type of rhythmic relationship established between the voices:
 |
polirritmia libre   |
The freest case is the superposition of two or more distinct successions of varied iT.
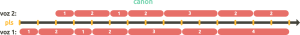 |
polirritmia en canon   |
We can also superimpose two or more voices that share an identical succession of iT, one being the original voice, and the rest, displaced voices. This is what we commonly know as canon, and to generate it we use the displacement operation. In these cases, the displacement interval is very important and will generate different effects depending on whether we shorten or lengthen it.
 |
polirritmia imitativa   |
A case similar to the canon is that the displaced succession is not identical to the original, but an imitation with slight variations, still perceiving the parallelism between both voices.
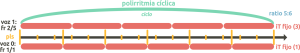 |
polirritmia cíclica   |
Another case is cyclic polyrhythm, where each voice is defined by a fixed temporal interval (whose value remains the same throughout the cycle) and a fraction. This generates two or more fixed velocities that coincide every so often, creating cycles. This cyclical relationship can be expressed as a ratio.