Rhythmic cells are a rhythmic technique that uses the numerical values of the iTs to make different arithmetic combinations. Its use facilitates the study and practice of rhythmic language, while stimulating rhythmic composition and its development.
Temporal sets
What are temporal sets?
Sets are groupings of elements of the same type. In the case of the temporal dimension, we can group pulses, temporal intervals, fractions or bars, generating temporal successions or collections.
These two types of sets are closely related: we can make a succesion from a collection, or extract a collection from a succesion.

Temporal successions are sets of temporal elements of the same type whose order in time has been specified. Depending on the type of succession, the following aspects must be taken into account:
In temporal interval sequences, the different iT values can be freely ordered. Since they express distances or durations, their values are not limited to specific locations on the timeline. This type of successions can generate rhythmic patterns, and can also be worked or developed by means of rhythmic cells.
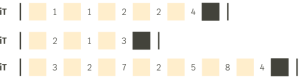
On the other hand, in the successions of absolute pulses o segment pulsesThese must always be ordered in ascending order, and it is not possible to repeat the same pulse. This is because they mark fixed positions on the timeline, where time always moves in the same direction.
In addition, these succesions must start with P(0), either to mark the beginning of a sound or of a silence. The same goes for the final pulse, which should also be included in the succession. This last pulse marks the end of the interval of the previous pulse, so we cannot assign a sound to it.
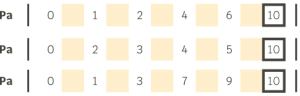
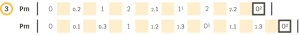
These two rules (ascending order and no repetition) also apply to successions of modular pulses,with the difference that the main number (which places the pulses within the succession of bars) returns to zero with each new bar. Therefore, although it may seem that certain pulses are repeated, in reality their locations are different, as we can see in the following examples.
In the successions of absolute pulses with fractioning we also apply the two previous rules, and we observe something similar to the previous case.Here the decimal numbers may coincide, but the same pulse or position within the succesion is not repeated either:
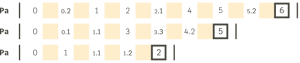
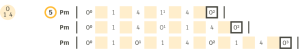
We can also make successions of modular pulses with fractioning:
As well as successions of fractions y successions of bars. We can call both structural successions, since they define the structure of the composition:
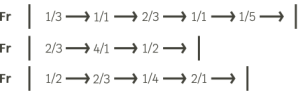
TEMPORAL COLLECTIONS
Temporal collections are sets of temporal elements of the same type in no particular order. We can make collections of temporal intervals, modular pulses, fractions or bars. In all four cases, Any order of the elements is possible and there is no limit to the number of repetitions.
This is an example of a collection of temporal intervals:
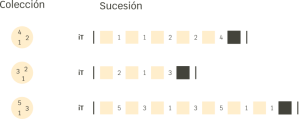
This is an example of a collection of modular pulses:
This would be an example of a collection of fractions:
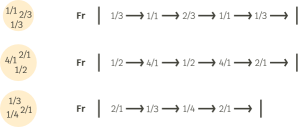
We cannot create collections of pulses with absolute numbering since they can only be sorted in ascending order and cannot be repeated.
RHYTHMIC PATTERN
A rhythmic pattern is a succession of iT that is repeated over time, generating a cycle with a determined length. Sometimes the temporal scale (a collection of pulses) can be used as a rhythmic pattern. Rhythmic cells or a combination of them can also be used as a pattern.
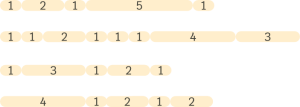
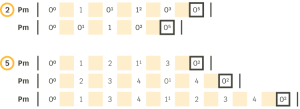
Rhythmic cells are categorized through collections of iT succesions that share the same length. For example, all iT succesions that add up to a length of 4 pulsations are part of the collection of cells of 4. These are: 1+1+1+1+1, 2+2, and 2+1+1+1.
Although each collection is made up of different combinations of iT, we end up perceiving them as a unit since they share the same groove . On the other hand, each of the successions of iTs is also a unit in itself – hence the concept of a cell. One way to look at it would be to think of iTs as syllables and cells as words.
The following are examples of collections of rhythmic cells, ordered from shortest to longest:
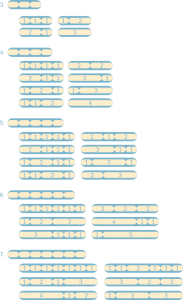
You can visit the table of rhythmic cells where you can see and listen to complete collections of cells of length 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.